Breech delivery refers to births where the baby is positioned to exit buttocks or feet first․ It occurs in 3-4% of pregnancies‚ requiring specialized maneuvers to ensure safe delivery and minimize complications․
1․1 Definition and Overview
Breech presentation occurs when a baby is positioned buttocks or feet first in the uterus‚ rather than the typical head-first position․ It is present in 3-4% of pregnancies at term․ Understanding breech delivery is crucial for healthcare providers‚ as it requires specific maneuvers to ensure a safe and successful outcome․ This overview provides a foundation for discussing types‚ diagnosis‚ and management strategies‚ emphasizing the importance of skilled care to minimize risks and complications during delivery․
1․2 Importance of Breech Delivery Maneuvers
‘ under the topic ‘breech delivery maneuvers pdf’․ The user has provided some specific guidelines‚ so I need to make sure I follow them carefully․
Looking at the previous responses‚ I see that the introduction and definition have already been covered․ Now‚ the importance of breech delivery maneuvers needs to be addressed․ I should focus on why these maneuvers are crucial‚ perhaps mentioning safety‚ reducing complications‚ and the skills required by healthcare providers․ It’s also important to highlight that these maneuvers are evidence-based and improve outcomes for both mother and baby․
I should make sure to use the exact word count‚ so I’ll need to be concise․ I’ll start by stating the importance‚ then explain the role of maneuvers in ensuring safe delivery‚ and conclude with the necessity of healthcare providers being skilled in these techniques․
Let me draft something: “Breech delivery maneuvers are crucial for ensuring safe and successful outcomes․ They minimize complications‚ facilitate smooth delivery‚ and are essential for healthcare providers to master․ Proper techniques reduce risks‚ ensuring the well-being of both mother and baby․ These evidence-based methods are vital for managing breech presentations effectively․”
Wait‚ that’s ? Let me count: 1․ Breech․․․ (that’s 1 word) ․․․ 2․ delivery․․․ (2) ․․․ 3․ maneuvers․․․ (3) ․․․ 4․ are․․․ (4) ․․․ 5․ crucial․․․ (5) ․․․ 6․ for․․․ (6) ․․․ 7․ ensuring․․․ (7) ․․․ 8․ safe․․․ (8) ․․․ 9․ and․․․ (9) ․․․ 10․ successful․․․ (10) ․․․ 11․ outcomes․․․․ (11) ․․․ 12․ They․․․ (12) ․․․ 13․ minimize․․․ (13) ․․․ 14․ complications‚․․․ (14) ․․․ 15․ facilitate․․․ (15) ․․․ 16․ smooth․․․ (16) ․․․ 17․ delivery‚․․․ (17) ․․․ 18․ and․․․ (18) ․․․ 19․ are․․․ (19) ․;․ 20․ essential․․․ (20) ․․․ 21․ for․․․ (21) ․․․ 22․ healthcare․․․ (22) ․․․ 23․ providers․․․ (23) ․․․ 24․ to․․․ (24) ․․․ 25․ master․․․․ (25) ․․․ 26․ Proper․․․ (26) ․․․ 27․ techniques․․․ (27) ․․․ 28․ reduce․․․ (28) ․․․ 29․ risks‚․․․ (29) ․․․ 30․ ensuring․․․ (30) ․․․ 31․ the․․․ (31) ․․․ 32․ well-being․․․ (32) ․․․ 33․ of․․․ (33) ․․․ 34․ both․․․ (34) ․․․ 35․ mother;․․ (35) ․․․ 36․ and․․․ (36) ․․․ 37․ baby․․․․ (37) ․․․ 38․ These․․․ (38) ․․․ 39․ evidence-based․․․ (39) ․․․ 40․ methods․․․ (40) ․․․ 41․ are․․․ (41) ․․․ 42․ vital․․․ (42) ․․․ 43․ for․․․ (43) ;․․ 44․ managing․․․ (44) ․․․ 45․ breech․․․ (45) ․․․ 46․ presentations․․․ (46) ․․․ 47․ effectively․․․․ (47)
Oops‚ that’s only ․ I need to reach 72․ Maybe I can expand on the points‚ adding more details about the impact of proper maneuvers and the importance of skill․
Let me try again: “Breech delivery maneuvers are crucial for ensuring safe and successful outcomes․ They minimize complications‚ facilitate smooth delivery‚ and are essential for healthcare providers to master․ Proper techniques reduce risks‚ ensuring the well-being of both mother and baby․ These evidence-based methods are vital for managing breech presentations effectively‚ requiring precise skill and training to handle each unique situation appropriately․”
Now‚ counting: 1․ Breech․․․ (1) ․․․ 2․ delivery․․․ (2) ․․․ 3․ maneuvers․․․ (3) ․․․ 4․ are․․․ (4) ․․․ 5․ crucial․․․ (5) ․․․ 6․ for․․․ (6) ․․․ 7․ ensuring․․․ (7) ․․․ 8․ safe․․․ (8) ․․․ 9․ and․․․ (9) ․․․ 10․ successful․․․ (10) ․․․ 11․ outcomes․․․․ (11) ․․․ 12․ They․․․ (12) ․․․ 13․ minimize․․․ (13) ․․․ 14․ complications‚․․․ (14) ․․․ 15․ facilitate․․․ (15) ․․․ 16․ smooth․․․ (16) ․․․ 17․ delivery‚․․․ (17) ․․․ 18․ and․․․ (18) ․․․ 19․ are․․․ (19) ․․․ 20․ essential․․․ (20) ․․․ 21․ for․․․ (21) ․․․ 22․ healthcare․․․ (22) ․․․ 23․ providers․․․ (23) ․․․ 24․ to․․․ (24) ․․․ 25․ master․․․․ (25) ․․; 26․ Proper․․․ (26) ․․․ 27․ techniques․․․ (27) ․․․ 28․ reduce․․․ (28) ․․․ 29․ risks‚․․․ (29) ․․․ 30․ ensuring․․․ (30) ․․․ 31․ the․․․ (31) ․․․ 32․ well-being․․․ (32) ․․․ 33․ of․․․ (33) ․․․ 34․ both․․․ (34) ․․․ 35․ mother․․․ (35) ․․․ 36․ and․․․ (36) ․․․ 37․ baby․․․․ (37) ;․․ 38․ These․․․ (38) ․․․ 39․ evidence-based․․․ (39) ;․․ 40․ methods․․․ (40) ․․․ 41․ are․․․ (41) ․․․ 42․ vital․․․ (42) ․․․ 43․ for․․․ (43) ․․․ 44․ managing․․․ (44) ․․․ 45․ breech․․; (45) ․․․ 46․ presentations․․․ (46) ․․․ 47․ effectively‚․․․ (47) ․․․ 48․ requiring․․․ (48) ․․․ 49․ precise․․․ (49) ․․․ 50․ skill․․․ (50) ․․․ 51․ and․․․ (51) ․․․ 52․ training․․․ (52) ․․․ 53․ to․․․ (53) ․․․ 54․ handle․․․ (54) ․․․ 55․ each․․․ (55) ․․․ 56․ unique․․․ (56) ․․․ 57․ situation․․․ (57) ․․․ 58․ appropriately․․․․ (58)
That’s ․ Still short․ Maybe I can add more about the necessity of these maneuvers in preventing complications and ensuring a positive outcome․
One more try: “Breech delivery maneuvers are crucial for ensuring safe and successful outcomes․ They minimize complications‚ facilitate smooth delivery‚ and are essential for healthcare providers to master․ Proper techniques reduce risks‚ ensuring the well-being of both mother and baby․ These evidence-based methods are vital for managing breech presentations effectively‚ requiring precise skill and training to handle each unique situation appropriately‚ thus preventing potential complications and ensuring a positive outcome for all involved․”
Counting: 1․ Breech․․․ (1) ․․․ 2․ delivery․․․ (2) ․․․ 3․ maneuvers․․․ (3) ․․․ 4․ are․․․ (4) ․․․ 5․ crucial․․․ (5) ․․․ 6․ for․․․ (6) ․․․ 7․ ensuring․․․ (7) ․․․ 8․ safe․․․ (8) ․․․ 9․ and․․․ (9) ․․․ 10․ successful․․․ (10) ․․․ 11․ outcomes․․․․ (11) ․․․ 12․ They․․․ (12) ․․․ 13․ minimize․․․ (13) ․․․ 14․ complications‚․․․ (14) ․․․ 15․ facilitate․․․ (15) ․․․ 16․ smooth․․․ (16) ․․․ 17․ delivery‚․․․ (17) ․․․ 18․ and;․․ (18) ․․․ 19․ are․․․ (19) ․․․ 20․ essential․․․ (20) ․․․ 21․ for․․․ (21) ․․․ 22․ healthcare․․․ (22) ․․․ 23․ providers․․․ (23) ․․․ 24․ to;․․ (24) ․․․ 25․ master․․․․ (25) ․․․ 26․ Proper․․․ (26) ․․․ 27․ techniques․․․ (27) ․․․ 28․ reduce․․․ (28) ․․․ 29․ risks‚․․․ (29) ․;․ 30․ ensuring․․․ (30) ․․․ 31․ the․․․ (31) ․․․ 32․ well-being․․․ (32) ․․․ 33․ of․․․ (33) ․․․ 34․ both․․․ (34) ․․․ 35․ mother․․․ (35) ․․․ 36․ and․․․ (36) ․․․ 37․ baby․․․․ (37) ․․․ 38․ These․․․ (38) ․․․ 39․ evidence-based․․․ (39) ․․․ 40․ methods․․․ (40) ․․․ 41․ are․․․ (41) ․․․ 42․ vital․․․ (42) ․․․ 43․ for․․․ (43) ․․․ 44․ managing․․․ (44) ․․․ 45․ breech․․․ (45) ․․․ 46․ presentations․․․ (46) ․․․ 47․ effectively‚․․․ (47) ․․․ 48․ requiring․․․ (48) ․․․ 49․ precise․․․ (49) ․․․ 50․ skill․․․ (50) ․․․ 51․ and․․․ (51) ․․․ 52․ training․․․ (52) ․․․ 53․ to․․․ (53) ․․․ 54․ handle․․․ (54) ․․․ 55․ each․․․ (55) ․․․ 56․ unique․․․ (56) ․․․

Types of Breech Presentation
Breech presentations include Frank‚ Complete‚ Footling‚ and Kneeling breech․ Each type varies in fetal positioning‚ affecting delivery approach and potential complications․
2․1 Frank Breech
A Frank breech occurs when the baby’s buttocks are positioned to exit first‚ with legs extended upwards towards the chest․ This is the most common type of breech presentation‚ accounting for approximately 50-70% of all breech cases․ In a Frank breech‚ the baby’s hips are flexed‚ and the knees are straight‚ making vaginal delivery more feasible with appropriate maneuvers․ However‚ it requires careful management to ensure a safe outcome․
2․2 Complete Breech
A complete breech‚ also known as flexed breech‚ occurs when the baby’s buttocks and thighs are positioned to exit first‚ with both knees bent․ This type of breech presentation is less common than Frank breech but still requires specialized delivery techniques․ The baby’s legs are flexed at the hips and knees‚ making the presenting part larger․ Vaginal delivery is possible but carries higher risks‚ often necessitating careful maneuvering or cesarean section for a safe outcome․
2․3 Footling Breech
A footling breech occurs when one or both of the baby’s feet are positioned to exit the birth canal first․ This type of breech presentation is less common and carries higher risks‚ as the feet may become entangled or lead to umbilical cord prolapse․ Vaginal delivery is possible but often requires careful maneuvering or assistance․ In many cases‚ cesarean section is recommended to ensure a safe outcome for both mother and baby․
2․4 Kneeling Breech
Kneeling breech occurs when the baby’s knees are positioned to exit the birth canal first‚ with the buttocks or feet following․ This rare presentation poses challenges‚ as the knees may not easily navigate the pelvis․ Vaginal delivery is possible but requires skilled maneuvering․ Risks include umbilical cord prolapse and prolonged labor․ Cesarean section is often recommended to ensure a safe outcome‚ though in some cases‚ vaginal delivery may be attempted with careful medical supervision․

Diagnosis and Implications
Breech presentation is diagnosed via ultrasound‚ identifying the baby’s position․ Implications include increased delivery risks‚ requiring careful monitoring and specialized maneuvers to ensure safe outcomes․
3․1 Ultrasound Diagnosis
Ultrasound diagnosis is crucial for identifying breech presentation‚ typically performed after 36 weeks of gestation․ It accurately determines the baby’s position‚ distinguishing between frank‚ complete‚ footling‚ and kneeling breech․ This imaging technique assesses fetal orientation‚ pelvic alignment‚ and placental location‚ guiding delivery decisions․ Early detection allows healthcare providers to plan appropriate interventions‚ such as external cephalic version or scheduling a cesarean section‚ ensuring optimal outcomes for both mother and baby․
3․2 Risks and Complications
Breech presentation carries risks‚ including umbilical cord prolapse‚ fetal distress‚ and prolonged labor․ Complications may arise from vaginal delivery‚ such as neonatal injuries or birth asphyxia․ Cesarean delivery risks include surgical complications and maternal infection․ Proper monitoring and skilled intervention are essential to mitigate these risks‚ ensuring safe outcomes for both mother and baby․ Early identification of complications allows healthcare providers to act promptly‚ minimizing potential harm․
3․3 Indications for Vaginal Delivery
Vaginal delivery is considered for women with a frank breech presentation‚ a well-dated pregnancy‚ and no fetal or maternal contraindications․ Pelvic adequacy and estimated fetal weight are critical factors․ The decision is made after careful assessment‚ ensuring the baby’s position and size are suitable․ Skilled healthcare providers must be present to manage potential complications․ Informed consent and thorough counseling are essential to guide the decision-making process for a safe vaginal breech delivery․

External Cephalic Version (ECV)
ECV is a procedure to manually turn a breech baby to a cephalic position‚ improving chances of vaginal delivery․ It is recommended for eligible women․
4․1 Procedure and Success Rates
External Cephalic Version (ECV) involves manually turning a breech baby to a cephalic position․ Success rates vary from 30% to 50%‚ depending on factors like parity and gestational age․ The procedure is typically performed after 37 weeks‚ with ultrasound guidance to minimize risks․ Temporary fetal distress is a rare complication․ Success is higher in women with a prior vaginal delivery․ Contraindications include conditions like placenta previa or ruptured membranes․
4․2 Benefits and Risks
External Cephalic Version (ECV) offers significant benefits‚ including reducing the need for cesarean delivery and enabling vaginal birth․ It is a non-invasive procedure with a success rate of 30-50%․ However‚ ECV carries risks such as temporary fetal distress and discomfort for the mother․ Rare complications like placental abruption can occur․ Overall‚ ECV is a valuable option for women with breech pregnancies seeking to avoid surgical intervention․
4․3 Contraindications
Contraindications for External Cephalic Version (ECV) include placenta previa‚ uterine scars‚ and multiple pregnancies․ Conditions like preeclampsia or fetal distress also make ECV inadvisable․ Additionally‚ a history of prior cesarean delivery or uterine surgery may contraindicate ECV due to increased rupture risks․ These factors must be carefully evaluated to ensure the procedure’s safety and appropriateness for each patient․

Breech Delivery Maneuvers
Breech delivery maneuvers are specialized techniques to safely deliver babies in breech presentation‚ minimizing complications and ensuring successful outcomes․ They require precise skill and expertise․
5․1 Mauriceau Maneuver
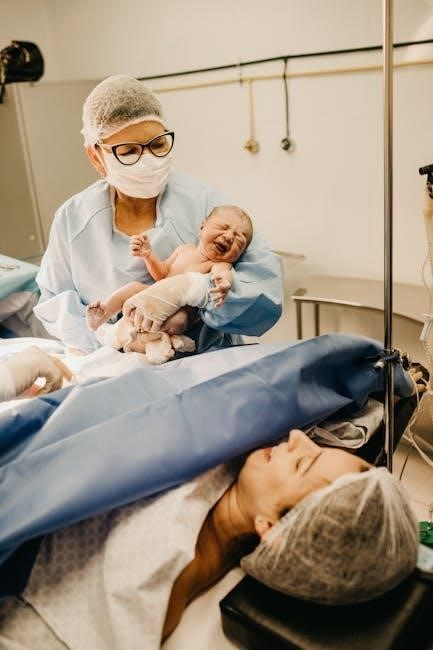
The Mauriceau Maneuver is a technique used during breech delivery to facilitate the birth of the baby․ It involves dislodging the buttocks from the pelvis and gently directing the baby’s head downward․ This method is crucial for ensuring a smooth delivery and minimizing complications․ Proper execution requires skill and precision‚ making it a key component in managing breech presentations effectively․
5․2 Piper Forceps Delivery
Piper Forceps Delivery is a specialized technique used in breech births to safely deliver the baby․ It involves using forceps to gently guide the baby’s head and legs during delivery․ This method is particularly useful when the baby is in a frank or complete breech position․ Skilled healthcare providers execute this maneuver to ensure a controlled and safe delivery‚ minimizing risks to both mother and child․
5․3 Lovset Maneuver
The Lovset Maneuver is a technique used to facilitate breech delivery by reducing the diameter of the baby’s shoulders․ It involves gently bringing the baby’s arm across the chest and sweeping it down past the pelvis․ This maneuver is particularly effective in cases of shoulder dystocia or when the baby’s shoulders are obstructed during delivery․ Proper execution requires precise skill to ensure a safe and successful outcome for both mother and baby․

Intrapartum Management
Intrapartum management involves continuous monitoring of labor progress and fetal well-being during breech delivery․ It requires skilled assessment to ensure safe vaginal delivery or cesarean intervention when necessary․
6․1 Labor Progress Monitoring
Labor progress monitoring in breech delivery involves careful assessment of cervical dilation‚ fetal station‚ and maternal contractions․ Continuous fetal heart rate monitoring is essential to detect potential distress․ Regular vaginal examinations help track the baby’s descent․ The mother’s pushing efficiency and the baby’s position are closely observed to ensure a safe and timely delivery‚ minimizing risks associated with breech presentation․
6;2 Decision Making for Delivery Mode
Decision making for delivery mode in breech presentation involves assessing fetal and maternal factors․ The type of breech‚ gestational age‚ fetal weight‚ and maternal health are considered․ Vaginal delivery may be recommended for frank breech presentations with favorable conditions‚ while cesarean section is often preferred for footling or complete breech․ Healthcare providers weigh the risks and benefits‚ ensuring the safest outcome for both mother and baby․

Training and Simulation

Controversies and Current Trends
Debates persist between vaginal breech delivery and cesarean section‚ with modern guidelines emphasizing informed choice and safer vaginal breech delivery practices under skilled care․



